|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Add/Edit Diagnosis |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Add/Edit Diagnosis |
  
|
To add or edit a diagnosis click the add ![]() or the edit
or the edit ![]() icon on the Results table.
icon on the Results table.
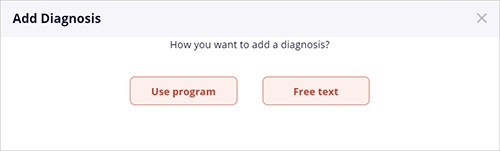
In the add/edit diagnosis popup, select 'Use program' or 'Free text'. When adding a diagnosis, selecting 'Use program' opens the patient diagnostic process Start page. When editing a diagnosis, selecting 'Use program' opens the diagnosis criteria page with your previous entries. Alternatively, If you select the 'Free text' option to add a diagnosis, the program opens the 'Add/Edit Diagnosis' empty form.
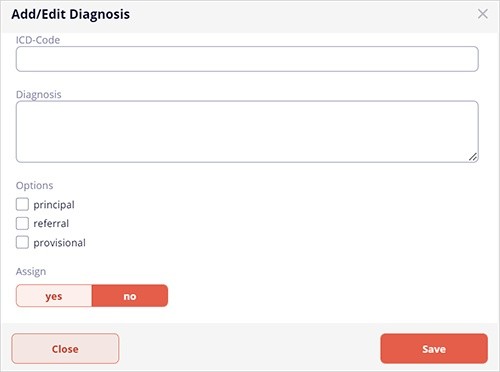
When you select to edit diagnosis with the 'Free text' option, the program opens the diagnosis form with the diagnosis record.
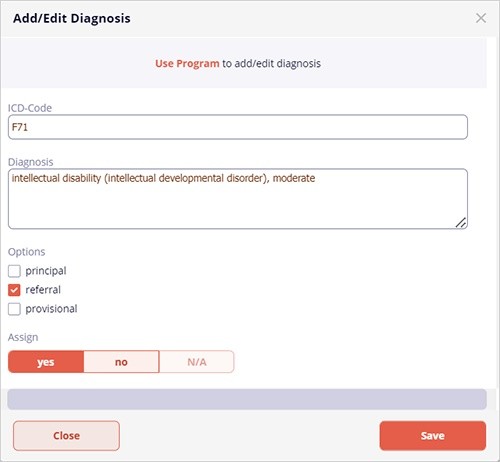
You can edit the diagnosis ICD-code and name, select one or more of the diagnosis options, and decide if the diagnosis should be currently assigned to the patient.
Diagnosis options:
When more than one diagnosis for an individual is given in an inpatient setting, the principal diagnosis is the condition established to be chiefly responsible for occasioning the admission of the individual. When more than one diagnosis is given for an individual in an outpatient setting, the referral diagnosis is the condition that is chiefly responsible for the ambulatory care medical services received during the visit. In most cases, the principal diagnosis or the referral diagnosis is also the main focus of attention or treatment. The specifier provisional diagnosis can be used when there is a strong presumption that the full criteria will ultimately be met for a disorder but not enough information is available to make a firm diagnosis. For example, when an individual is unable to give an adequate history, or when the diagnosis depends exclusively on the duration of illness. The clinician can indicate the diagnostic uncertainty by recording "(provisional)". When one or more of the options is selected, the diagnosis name is followed by the qualifying phrase (principal), (referral), or (provisional).
Generally, the diagnosis free-text form is intended to provide the clinician with maximum control over the diagnosis record. The final diagnosis is made based on the clinical interview, criteria text descriptions, and clinician judgment.